Introducing How Car AC System Works
Understanding how your car’s AC system works is essential for maintaining comfort during those hot summer drives. The car AC system is a complex marvel of modern automotive engineering, designed to provide cool air inside your vehicle, regardless of the outside temperature. This blog will explain the fundamental principles behind the car AC system, its main components, and how each part contributes to the cooling process.
The Basic Principles of Car AC System
At its core, the car AC system operates on the principles of refrigeration. The system works by removing heat and moisture from the air inside your car and expelling it outside, thus lowering the interior temperature. Refrigerant, a unique fluid that transitions from a gas to a liquid and back again during the cooling cycle, is circulated during this operation.
Main Components of a Car AC System
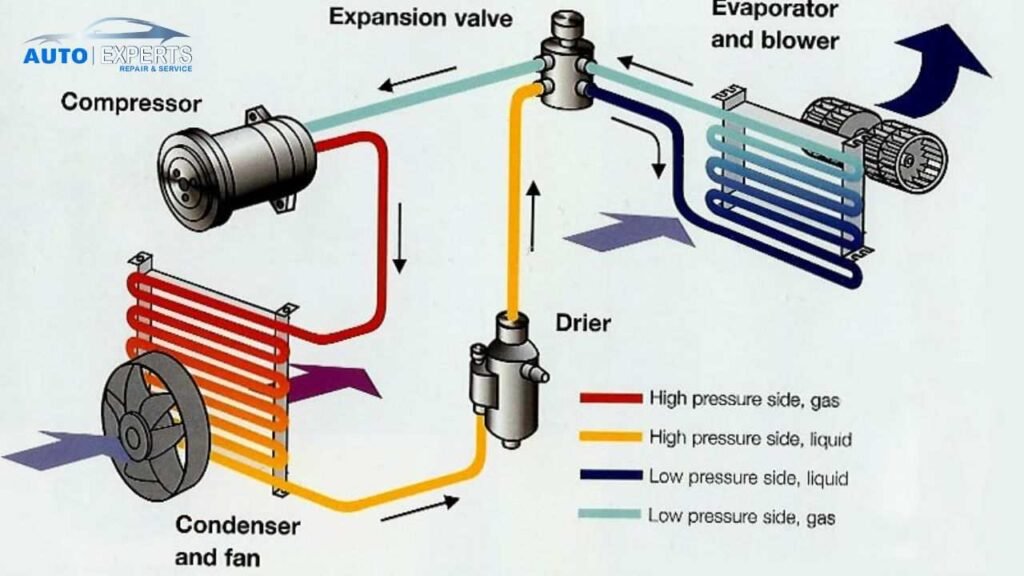
Knowing the major parts of an automobile air conditioning system is essential to understand how it operates. The refrigerant, compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve are some of these parts.
1. Compressor
The compressor is often considered the heart of the AC system. It is driven by a belt from the engine of the car. The compressor’s primary function is to pressurize the refrigerant and circulate it through the AC system. It draws in low-pressure refrigerant gas from the evaporator and compresses it into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
2. Condenser
The high-pressure, high-temperature gas from the compressor flows into the condenser. The condenser is usually located at the front of the car, near the radiator. The gas cools and condenses into a high-pressure liquid as it travels through the condenser, releasing heat to the surrounding air.
3. Expansion Valve
After that, the expansion valve or orifice tube receives the high-pressure liquid refrigerant. This part is in charge of managing the refrigerant flow into the evaporator. The expansion valve allows the high-pressure liquid refrigerant to expand and drop in pressure as it enters the evaporator.
4. Evaporator
Usually, the evaporator is found inside the dashboard of the vehicle. Heat from the car’s interior is absorbed by the low-pressure refrigerant as it goes into the evaporator, causing it to evaporate into a low-pressure gas. The air that the blower motor forces into the car’s cabin is cooled by this process.
5. Refrigerant
The refrigerant is the fluid that cycles through the AC system, absorbing and releasing heat as it changes from a liquid to a gas and back again. Common refrigerants used in car AC systems include R-134a and the more environmentally friendly R-1234yf.
The Cooling Cycle Explained
Now that we’ve identified the main components, let’s dive into how they work together in the cooling cycle.
1. Compression
The cycle begins with the compressor. When you turn on your car’s AC, the compressor kicks into action, compressing the refrigerant gas into a high-pressure, high-temperature state. This compression raises the refrigerant’s temperature significantly.
2. Condensation
The high-pressure gas then flows to the condenser. Moving through the condenser’s coils releases heat to the outside air, causing the refrigerant to cool and condense into a high-pressure liquid. This step is crucial because it allows the refrigerant to lose the heat absorbed from inside the car.
3. Expansion
The expansion valve is next in line for the high-pressure liquid refrigerant to reach. The valve regulates how much refrigerant is allowed to pass through to the evaporator. The refrigerant expands and loses pressure as it moves through the valve. As the refrigerant enters the evaporator, it cools quickly due to the abrupt pressure drop.
4. Evaporation
Inside the evaporator, the cold, low-pressure refrigerant absorbs heat from the car’s cabin air. The refrigerant turns into a gas as it absorbs heat. The blower motor then blows the cooled air through the evaporator and into the car’s interior, providing that refreshing cool breeze.
5. Recirculation
The now warm, low-pressure refrigerant gas returns to the compressor, and the cycle repeats. This continuous cycle keeps the air inside your car cool and comfortable.
Additional Components and Features
In addition to the primary components, modern car AC systems may include several additional features and components designed to improve efficiency and comfort.
1. Receiver-Drier or Accumulator
The receiver-drier or accumulator is a component that removes moisture from the refrigerant. Moisture can cause damage to the AC system, so this component ensures the refrigerant remains dry. The receiver-drier is typically found in systems with a thermal expansion valve, while accumulators are found in systems with an orifice tube.
2. AC Control Panel
The AC control panel inside your car allows you to adjust the temperature, fan speed, and airflow direction. It also includes buttons for turning the AC on or off and for activating the recirculation mode, which reuses the air inside the car to improve cooling efficiency.
3. Cabin Air Filter
The cabin air filter helps clean the air that enters your car’s interior. It traps dust, pollen, and other particles, ensuring that the air you breathe is clean. A clogged filter can reduce the efficiency of your AC system, so it’s important to replace it regularly.
Common Issues and Maintenance Tips
Like any other system in your car, the AC system can encounter problems. Here are some common issues and maintenance tips to keep your car’s AC running smoothly.
1. Refrigerant Leaks
Refrigerant leaks are a frequent problem with automobile air conditioners. These leaks can occur in any part of the system and result in reduced cooling performance. If you notice your AC is not as cold as it used to be, a refrigerant leak might be the cause. A qualified expert can find and fix these leaks.
2. Faulty Compressor
One essential part of the AC system is the compressor. The entire system could fail if it fails. Signs of a faulty compressor include strange noises, leaks, or the AC not blowing cold air. It is possible to identify and avoid compressor problems with routine maintenance.
3. Clogged Condenser
Debris might clog the condenser, reducing its efficiency. If the condenser cannot release heat properly, the refrigerant won’t cool down as it should. Regularly checking and cleaning the condenser can prevent this problem.
4. Dirty Evaporator
A dirty evaporator can also affect the performance of your AC system. Dust and dirt can accumulate on the evaporator’s surface, reducing its ability to absorb heat. Cleaning or replacing the cabin air filter can help keep the evaporator clean.
5. Electrical Issues
Electrical issues can cause problems with the AC system. Faulty wiring, blown fuses, or a malfunctioning control panel can prevent the AC from working correctly. Regularly inspecting the electrical components can help prevent these issues.
Tips for Maintaining Your Car’s AC System
Maintaining your car’s AC system is essential for ensuring it works efficiently. Here are some tips to help you keep your AC system in top shape:
- Check Refrigerant Levels Frequently: Insufficient refrigerant might cause a decrease in cooling efficiency. Have your refrigerant levels checked and topped up by a professional if necessary.
- Inspect Belts and Hoses: Check the belts and hoses connected to the compressor for any signs of wear or damage. Replace them if needed.
- Keep the Condenser Clean: Make sure the condenser is free of debris and dirt. A clean condenser helps the refrigerant cool down more effectively.
- Replace the Cabin Air Filter: A clean cabin air filter improves air quality and AC performance. Following the maintenance schedule for your car, replace it.
- Run the AC Regularly: Running the AC for a few minutes every week, even during the winter, helps keep the system lubricated and prevents seals from drying out.
- Have Regular Inspections: Regular AC system inspections by a professional can help detect and address potential issues before they become major problems.
How to Diagnose Car AC Problems
Diagnosing issues with your car’s air conditioning system can be simple if you follow these steps:
1. Check for Warm Air
When you turn on the AC, if it blows warm air instead of cold, this might indicate low refrigerant levels or a refrigerant leak. If needed, a qualified technician can inspect and refill the refrigerant.
2. Listen for Unusual Noises
Strange noises coming from the AC compressor can signal mechanical problems. Grinding, squealing, or clunking sounds are signs that the compressor might need repair or replacement.
3. Inspect the Condenser and Evaporator
Examine the condenser and evaporator for dirt or blockages. These components need to be clean to allow proper airflow and cooling. Debris can reduce efficiency and lead to overheating.
4. Check Electrical Connections
Faulty wiring or blown fuses can disrupt the AC system’s operation. Inspect all electrical connections and fuses to ensure they are intact and functioning correctly.
5. Monitor Refrigerant Levels
Low refrigerant levels are a common cause of AC problems. Ensure that the refrigerant is at the correct level and have a technician check for any leaks in the system.
6. Perform Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance, such as changing the cabin air filter and cleaning the AC components, can prevent many common issues. Schedule periodic inspections with a professional to keep your AC system in top condition.
How to Keep Car Cool Without AC
Keeping your car cool without relying on the AC is possible with these practical tips:
1. Park in the Shade
Whenever possible, park your car under trees, in a garage, or in shaded areas. This simple step prevents the car from heating up under direct sunlight.
2. Use Sunshades
Install sunshades on your windshield and windows to block sunlight. These reflective shields can significantly reduce the temperature inside your car.
3. Tint Your Windows
Tinted windows can minimize heat buildup by reducing the amount of sunlight that enters your car. Consider professional tinting for optimal results.
4. Open the Windows
While driving, open the windows to allow fresh air to circulate. This natural ventilation can help expel hot air and bring in cooler air from outside.
5. Use Ventilation Fans
Portable fans can enhance airflow inside your car. Clip them to your vents or place them strategically to direct air where it’s needed most.
6. Light-Colored Seat Covers
Choose steering wheel and seat covers in light colours. These reflect rather than absorb heat, helping to keep the interior cooler.
7. Maintain the Ventilation System
Ensure your car’s ventilation system is in good working order. Regular checks and cleaning can improve airflow and contribute to a cooler cabin.
Conclusion
Understanding how your car’s AC system works can help you appreciate the technology that keeps you cool during your drives. By knowing the key components and the cooling cycle, you can better maintain your AC system and address any issues that arise. Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial for ensuring your car’s AC system remains efficient and reliable, providing you with a comfortable driving experience year-round. Keep your car’s AC system in top shape, and enjoy the cool, refreshing air it delivers on those hot summer days.
For Top Digital Marketing Agency visit.